Neuroscience
Visualization of cell tracking, drug delivery, and pharmacodynamics in the brain
Contact UsCFT for Neuroscience Research
Cryo-Fluorescence Tomography (CFT) is a powerful imaging tool for neuroscience where fluorescence reporters can aid in visualization of cell tracking, drug delivery, and pharmacodynamics in the brain. CFT can be used to study the physiology, anatomy, and molecular biology of the brain. In addition, neurodegenerative diseases and other pathologies that affect different regions of the brain and neurological pathways can also be visualized.
Case Study: Intracerebral GFP-Expressing Cell Injection
Isolated Tissue Expression in Mice at 20µm
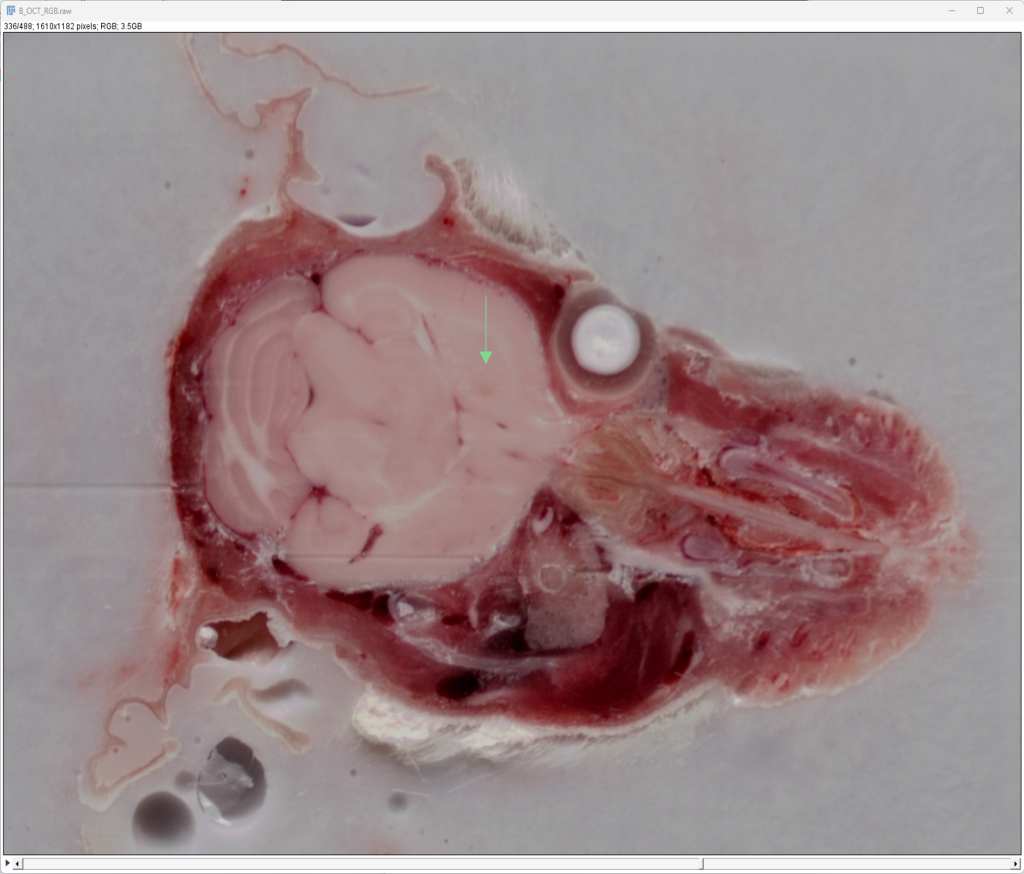
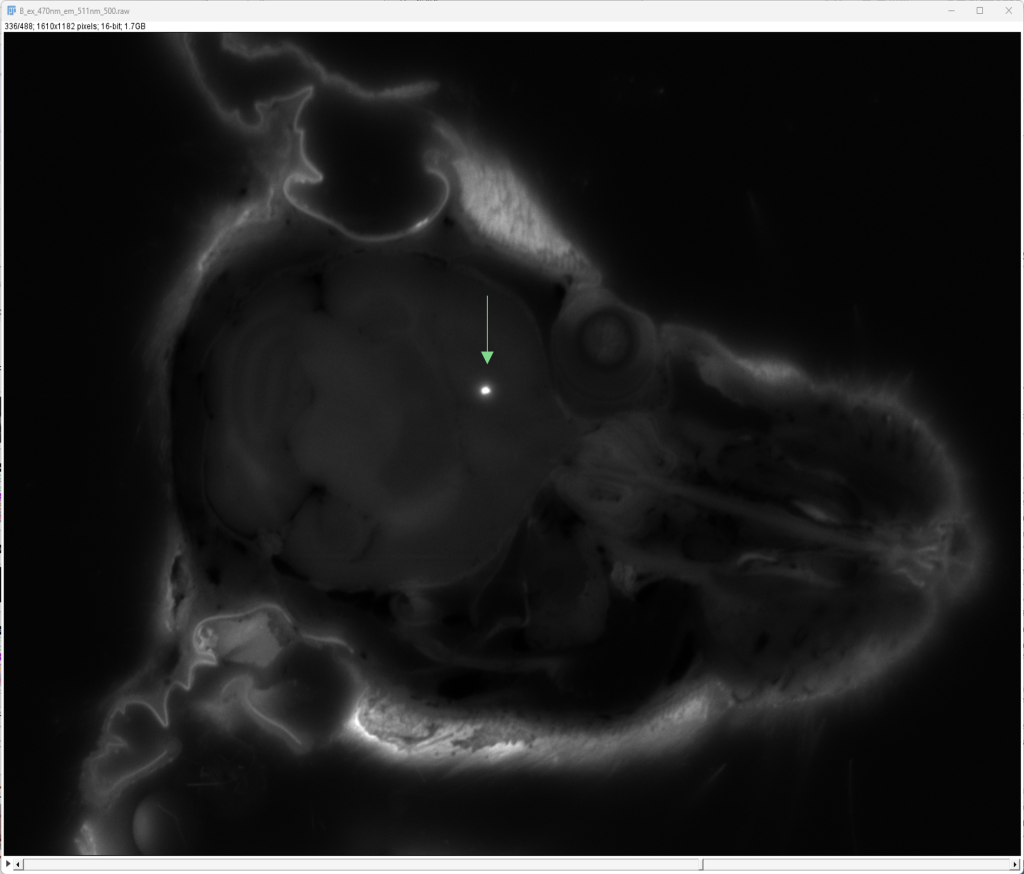
Findings: Imaging of isolated tissue samples with CFT provides higher resolution than whole-body. In this example, a mouse head was intracerebrally injected with GFP-expressing cells and imaged at 20µm.
Details:
- Imaging of mouse head at 20µm – higher resolution than whole-body CFT
- Unlike in vivo fluorescence, CFT works well with GFP.
- CFT is an ex vivo imaging technique and therefore not hindered by autofluorescence
-> Site of Injection
Images courtesy of Hernando Lopez Bertoni, Department of Neurology, John Hopkins School of Medicine
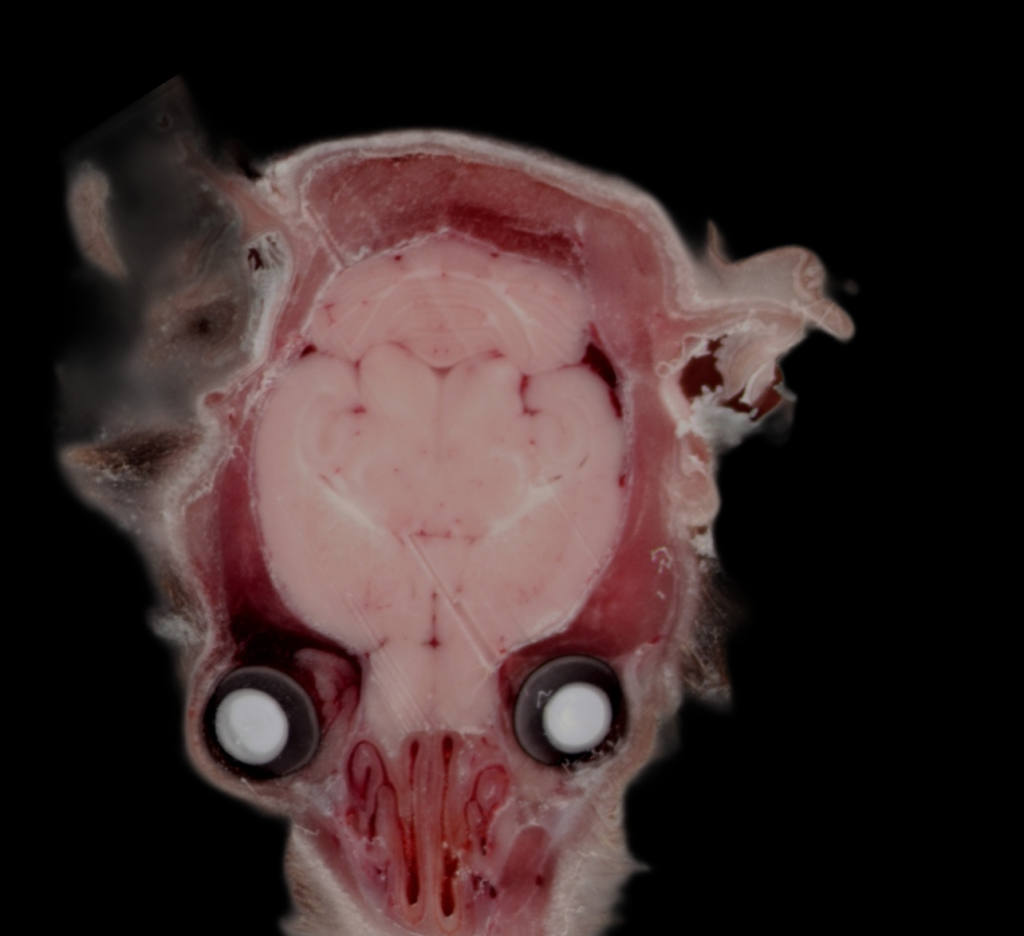
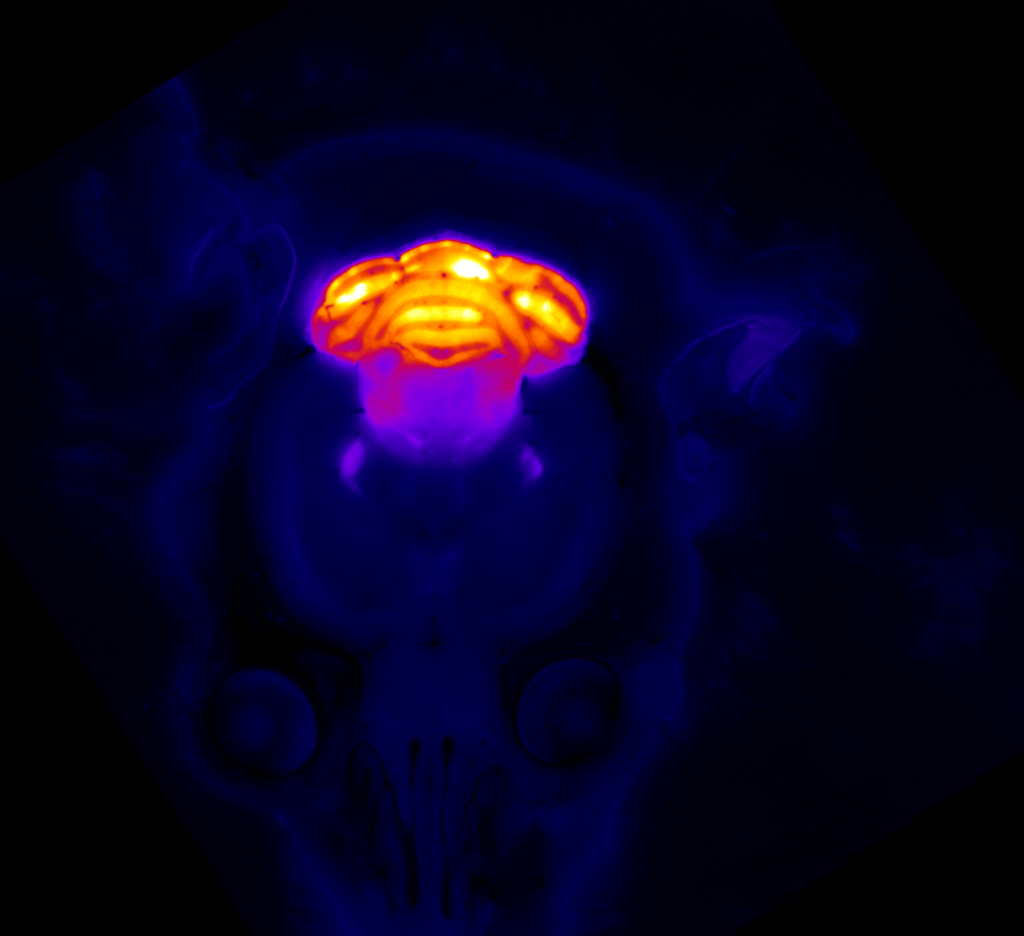
Case Study: Cell-specific Fluorescence Reporter Imaging
Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein (EGFP)
Details: GAD67-GFP (line G42) mice selectively express enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) in the parvalbumin (Pv)-expressing subclass of basket interneurons (soma, dendrites, and axons) and also in putative presynaptic boutons.